Working Papers

The reliability of classroom observations and student surveys in non-research settings: Evidence from Argentina
Both instruments can achieve relatively high reliability when averaged across raters and occasions, though observation reliability varies significantly based on how raters are assigned to teachers.

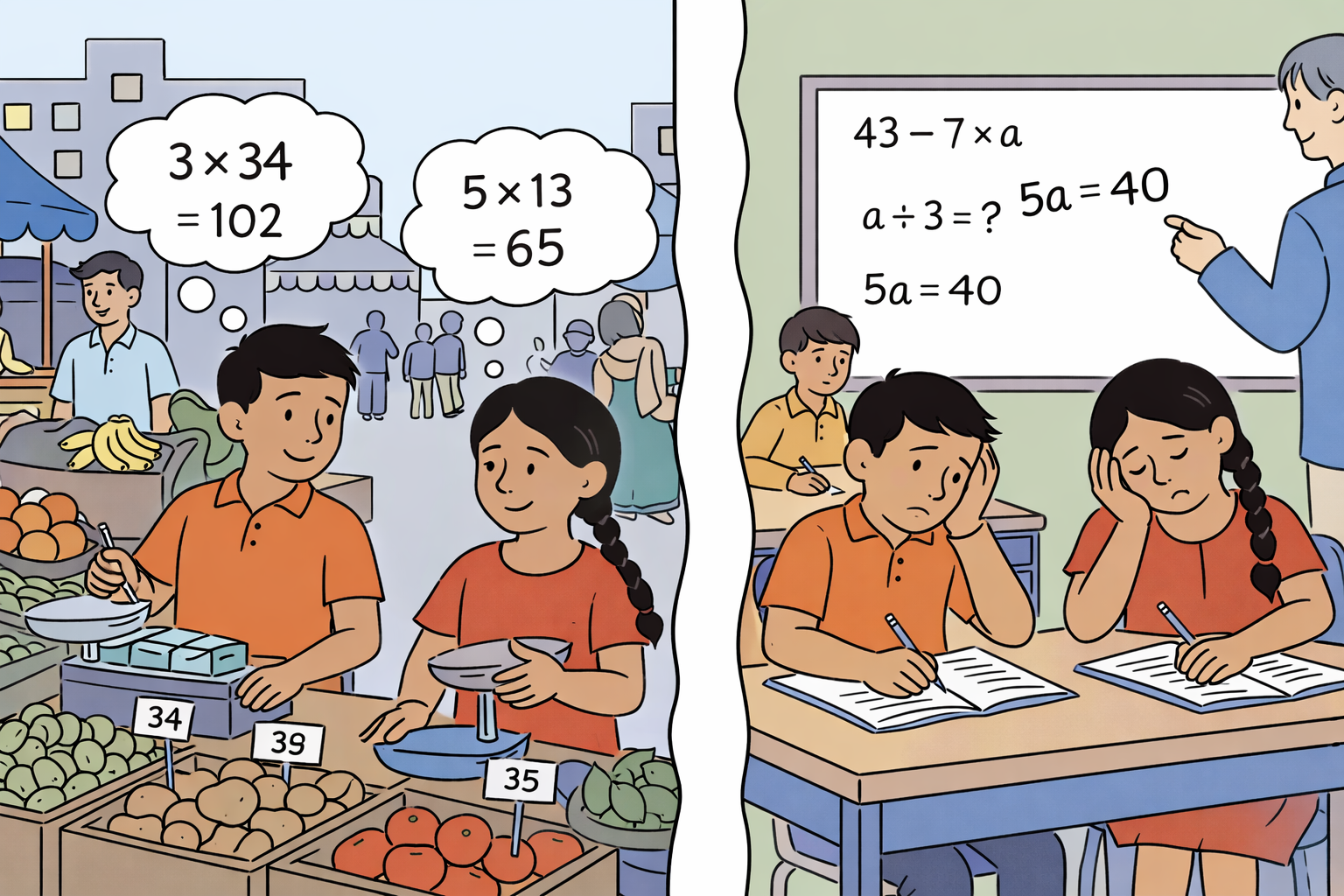
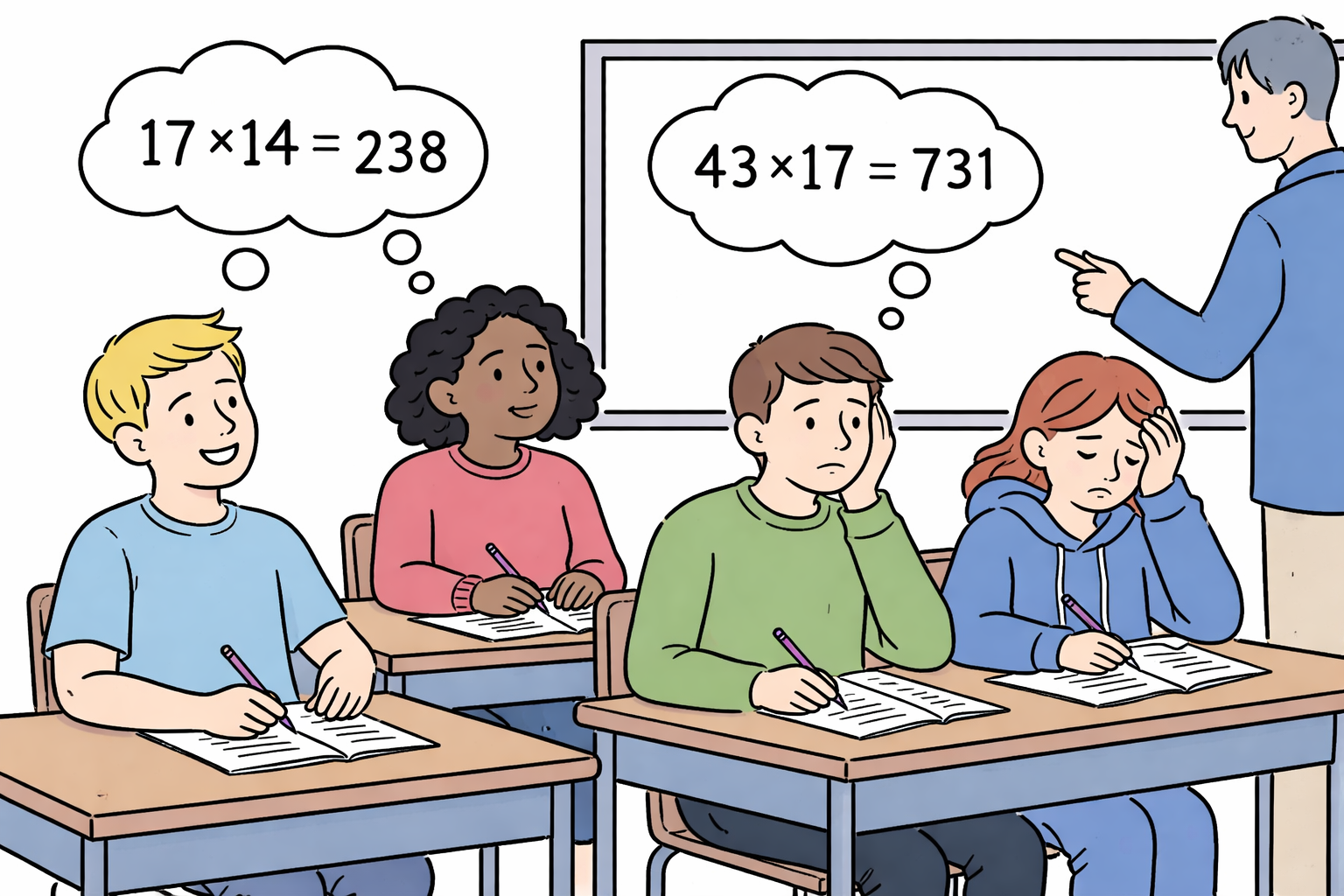
Leveraging complementarities between teachers' content knowledge and pedagogical supports: Experimental evidence from India
Fellows with strong content knowledge but minimal experience, when paired with training and coaching, substantially outperformed regular teachers in student math and science outcomes.

Does civic education impact primary-school students' civic outcomes? Experimental evidence from Liberia
The program improved factual civic knowledge substantially, particularly for lower-performing and rural students, but did not translate into increased civic engagement.
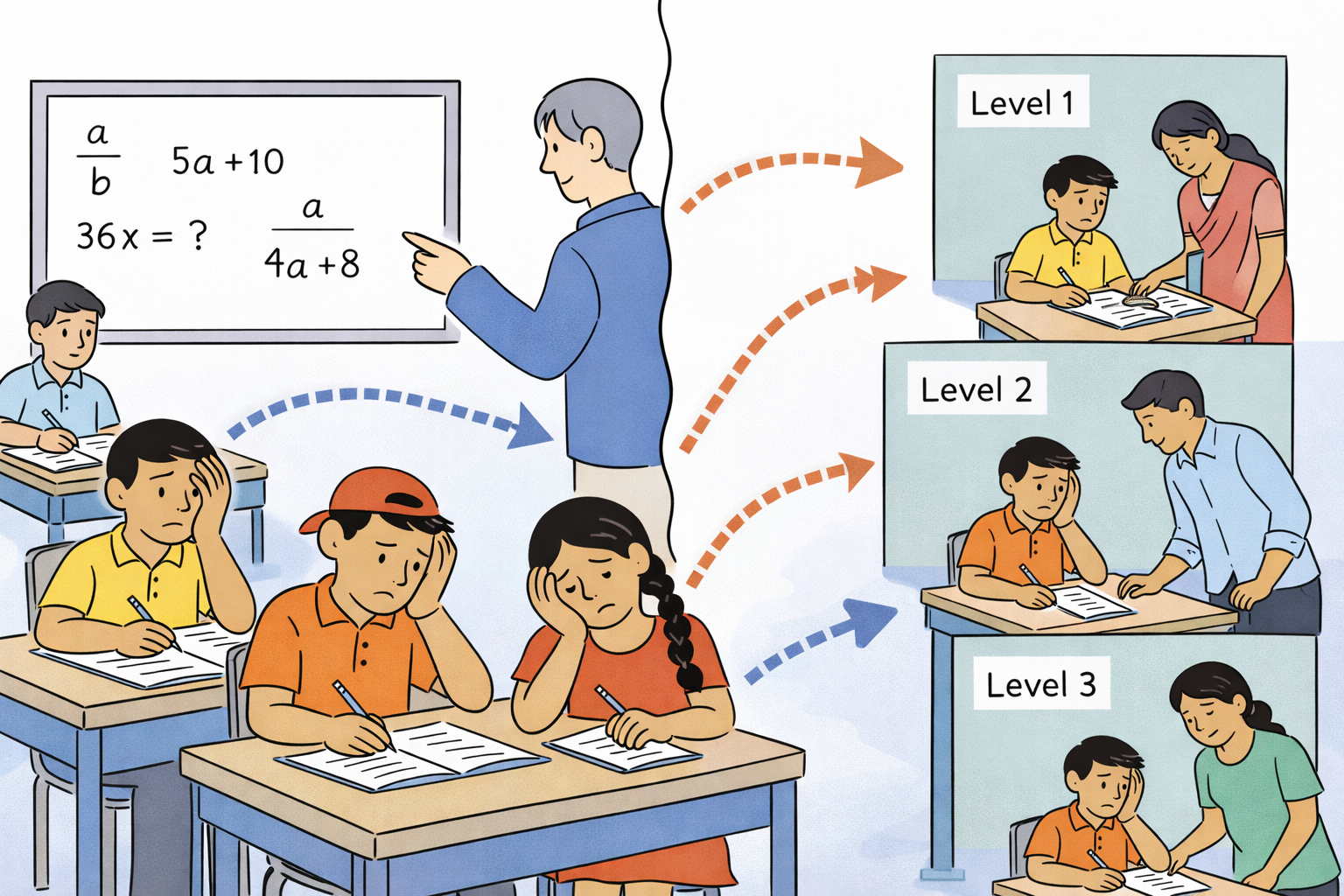
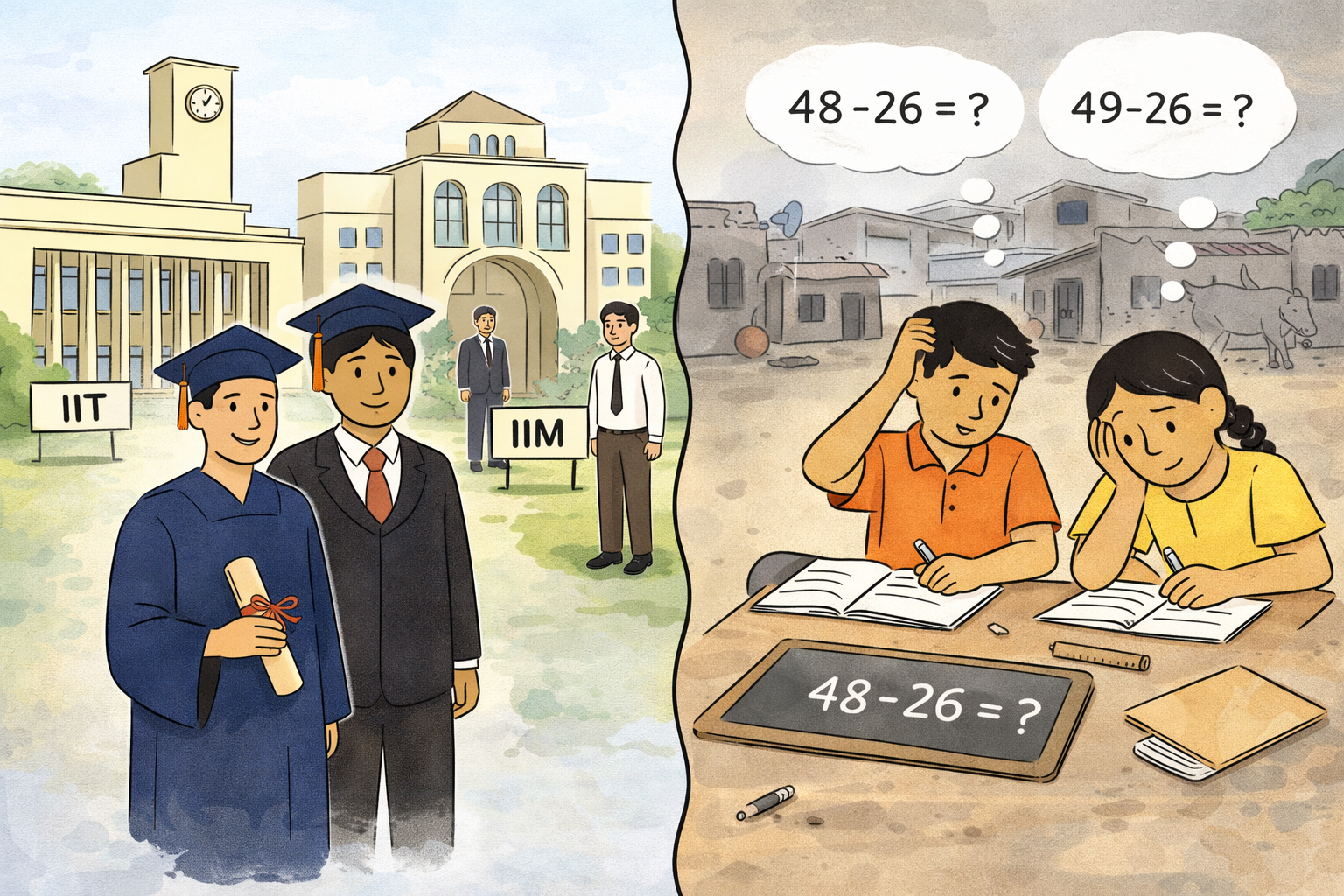
How can developing countries address heterogeneity in students' preparation for school? A review of the challenge and potential solutions
This review explores why schools struggle to accommodate diverse student preparation levels and proposes a conceptual framework for understanding systemic barriers to addressing this challenge.
Featured in: Brookings Institution, BOLD